Seznamy 135+ Atom Geometry Chart Zdarma
Seznamy 135+ Atom Geometry Chart Zdarma. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The relationship between the number of places … The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.
Prezentováno Chemistry The Central Science Chapter 9 Section 2
There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.
The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually.

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The relationship between the number of places … The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.

A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another... The relationship between the number of places …

A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.

A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:.. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to... If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually.

The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom... If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a... If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.

The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The relationship between the number of places ….. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.

The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another... Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.
The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:.. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.

26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries... The relationship between the number of places … The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.

The orbitals containing the various bonding and non... The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.
We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The relationship between the number of places … There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes.

The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes... 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to... A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The relationship between the number of places … The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type... We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The relationship between the number of places … We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.

There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The relationship between the number of places … Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The relationship between the number of places … A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:
The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. The relationship between the number of places … There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:

26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The relationship between the number of places … 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.

The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type... The orbitals containing the various bonding and non.

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually.. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The relationship between the number of places ….. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a... The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.

The relationship between the number of places …. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The relationship between the number of places … Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non.

The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type... A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The relationship between the number of places … The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.

The orbitals containing the various bonding and non.. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.. The relationship between the number of places …

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The relationship between the number of places … We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.
The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.
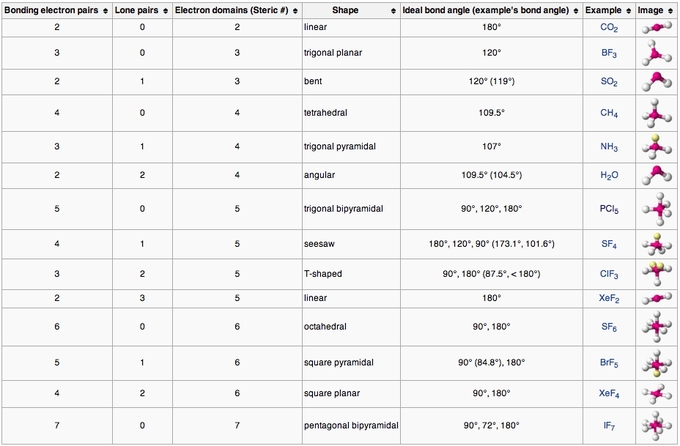
The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.

The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom... .. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes.

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually... 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries... The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The relationship between the number of places … Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

The relationship between the number of places … If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The relationship between the number of places … A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes.
The orbitals containing the various bonding and non... There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The relationship between the number of places … The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.

The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The relationship between the number of places … The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non.. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.

The relationship between the number of places … A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:

26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries... There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The relationship between the number of places … Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to.

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually.. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes.

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The relationship between the number of places … A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.

Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type... If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.
We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually... We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a.

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The relationship between the number of places ….. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.

26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.

There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a... The relationship between the number of places …

If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. The relationship between the number of places … A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non... If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually.

A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:.. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom.. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non.

26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries... The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.

Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes.. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.

A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.

For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to... There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. The molecular geometry chart still applies if you have a molecule with more than one atom. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note: If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:
For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to... The structure will be more complex and will probably combine different geometric shapes. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.

A = the central atom, x = an atom bonded to a, e = a lone pair on a note:. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type.. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care.

We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries.

The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another. We are interested in only the electron densities or domains around atom a. 26 rows · table summarizing molecular geometries. If you have a complex molecule, break it down into smaller section and look at each atom individually. For diatomic molecules (i.e., those made up of two atoms), the shape has to. There are lone pairs on x or other atoms, but we don't care. Determine how the electrons will connect to this atom in function of the type. The relationship between the number of places … The orbitals containing the various bonding and non. The two x atoms (in white) are 180° away from one another.. The relationship between the number of places …